The hair loss is a common concern affecting millions worldwide, impacting confidence and self-image. Fortunately, numerous treatments exist, but navigating them can be overwhelming. This article compares the two most clinically proven FDA-approved medications, Propecia (finasteride) and Rogaine (minoxidil), explores using them together, and delves into promising alternatives to help you make an informed decision.
Understanding the Enemy: Why Hair Happens
The primary culprit for most hair loss (androgenetic alopecia) is a combination of genetics and hormones. Specifically:
- DHT (Dihydrotestosterone): A potent derivative of testosterone, DHT miniaturizes hair follicles in genetically susceptible individuals (typically the crown and temples in men, diffuse thinning in women). This shortens the hair growth cycle, leading to finer, shorter hairs and eventual follicle dormancy.
- Genetics: Your inherited sensitivity to DHT dictates if and how aggressively this process occurs.
The Heavy Hitters: FDA-Approved Champions
1. Propecia (Finasteride) – The Hormone Blocker
- How it Works: An oral medication that inhibits the enzyme (5-alpha-reductase Type II) responsible for converting testosterone into DHT. By lowering scalp DHT levels significantly (by ~60-70%), it halts the miniaturization process and allows follicles to recover.
- Effectiveness:
- Stabilization: Highly effective at stopping further hair loss in the vast majority of men (~90%).
- Regrowth: Modest regrowth occurs in a significant minority (~65% see some improvement, often thicker hairs rather than full coverage). Best results are seen on the crown.
- Pros:
- Once-daily oral pill (convenient).
- Targets the root hormonal cause.
- High success rate for halting progression.
- Cons & Side Effects:
- For Men Only: Not approved for women (especially of childbearing age) due to risks of birth defects.
- Potential Side Effects: A small percentage (~1-2%) experience sexual side effects (decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, ejaculation disorders). These usually resolve upon stopping the medication. Rare reports of persistent side effects exist (“Post-Finasteride Syndrome”), though causality and prevalence are debated.
- Requires prescription.
- Results take 6-12 months to become apparent.
- Must be taken continuously to maintain benefits; stopping leads to reversal of gains within months.
- Best For: Men primarily concerned with stopping further hair loss, especially those with early to moderate androgenetic alopecia. Less effective for advanced baldness.
2. Rogaine (Minoxidil) – The Growth Stimulator
- How it Works: A topical solution or foam applied directly to the scalp. Its exact mechanism isn’t fully understood, but it’s believed to:
- Vasodilate blood vessels, increasing nutrient/oxygen delivery to follicles.
- Potentially prolong the anagen (growth) phase of hair.
- May stimulate follicles directly.
- Does not affect DHT levels.
- Effectiveness:
- Stabilization: Helps slow hair loss progression in many users.
- Regrowth: Can promote modest to moderate regrowth, particularly in the crown and vertex areas. Less effective for receding hairlines. Results vary significantly.
-
Pros:
- Available over-the-counter (OTC).
- Suitable for both men and women (different formulations/strengths).
- Works topically, minimizing systemic side effects.
- Can be used alongside other treatments.
-
Cons & Side Effects:
- Commitment: Requires twice-daily application indefinitely. Stopping causes reversal within months.
- Initial Shedding: Common in the first 2-8 weeks as miniaturized hairs are pushed out to make way for new growth. Can be alarming but is usually a positive sign.
- Scalp Irritation: Can cause dryness, itching, redness, or flaking (especially the liquid solution). Foam is generally better tolerated.
- Messiness: Can leave hair greasy or sticky (solution less so than foam).
- Results take 4-6 months to become noticeable; full results at 12+ months.
- Best For: Both men and women seeking regrowth potential, particularly on the crown/vertex. Good as a first-line OTC option or adjunct therapy.
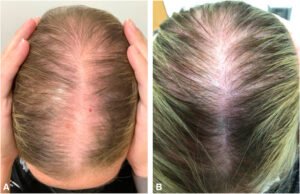
The Power Couple: Combining Propecia & Rogaine
Using both finasteride and minoxidil together is often considered the gold standard for medical treatment of male pattern baldness.
- Synergy: They work via different, complementary mechanisms. Finasteride attacks the hormonal cause (DHT), stopping the assault on follicles. Minoxidil directly stimulates follicles to grow hair.
- Effectiveness: Studies consistently show the combination is significantly more effective than either treatment alone for both halting hair loss and promoting regrowth. It offers the best chance for noticeable improvement.
- Considerations: Combines the pros and cons of both medications (oral pill + topical application, potential side effects from finasteride, commitment to minoxidil application). Requires a prescription for finasteride.
Beyond the Big Two: Exploring Alternatives
While Propecia and Rogaine have the strongest evidence, other options exist, often used as adjuncts or for those seeking alternatives:
-
Ketoconazole Shampoo (e.g., Nizoral):
- How: An antifungal shampoo with mild anti-androgen properties. May reduce scalp inflammation and slightly lower local DHT.
- Effectiveness: Modest. Best used as a supportive therapy alongside Propecia/Rogaine. Can help with scalp health and dandruff associated with hair loss.
- Pros: OTC, easy to use (2-3 times per week), minimal side effects.
- Cons: Not a standalone solution for significant regrowth.
-
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT):
- How: Uses red light devices (combs, helmets, caps) to stimulate cellular activity in hair follicles.
- Effectiveness: Modest. Some studies show it can stabilize loss and promote modest regrowth, similar to minoxidil. Results vary by device and consistency of use.
- Pros: Non-invasive, minimal side effects, suitable for men and women. Home devices available.
- Cons: Cost (devices can be expensive), requires consistent long-term use (multiple sessions per week), results take time (6+ months), efficacy debated.
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
- How: Involves drawing your blood, concentrating the platelets (rich in growth factors), and injecting them into the scalp.
- Effectiveness: Emerging evidence shows promise for improving hair density and thickness, particularly in early stages. Often requires multiple initial sessions and maintenance treatments.
- Pros: Uses your own cells, minimal risk of allergic reaction.
- Cons: Expensive, invasive (injections), requires multiple sessions, long-term efficacy data still evolving, not typically covered by insurance.
-
Microneedling (Dermarolling):
- How: Using a roller with tiny needles to create micro-injuries in the scalp, stimulating growth factors and potentially enhancing absorption of topical treatments like minoxidil.
- Effectiveness: Growing evidence suggests it can improve hair growth, especially when combined with minoxidil. Best results seen with consistent use (1-2 times per week).
- Pros: Can be done at home (with caution) or professionally, relatively low cost.
- Cons: Risk of infection/scarring if not done properly, can be uncomfortable, requires consistency.
-
Nutritional Supplements:
- How: Addressing potential deficiencies (Iron, Vitamin D, Zinc, Biotin) that can contribute to hair loss (though not usually the primary cause of androgenetic alopecia).
- Effectiveness: Only effective if a deficiency exists. Supplements like Viviscal, Nutrafol contain blends targeting hair health; evidence is mixed but some users report benefits.
- Pros: Generally safe, supports overall health.
- Cons: Unlikely to reverse genetic hair loss alone. Quality of products varies. Consult a doctor before starting high doses.
-
Hair Transplant Surgery:
- How: Surgical procedure moving healthy hair follicles (usually from the back/sides of the scalp) to balding areas.
- Effectiveness: The only permanent solution that restores natural-looking hair in the transplanted areas. Results are excellent when performed by a skilled surgeon.
- Pros: Permanent, natural results, addresses advanced baldness.
- Cons: Expensive, invasive surgery, requires recovery time, doesn’t stop loss in non-transplanted areas (often requires ongoing medication like finasteride to protect existing hair).
Key Takeaways & Choosing Your Path
Making Your Decision:
- Consult a Dermatologist: This is crucial. They can diagnose the type of hair loss, assess your stage, discuss medical history, and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan.
- Define Your Goal: Is your priority stopping further loss, regrowing hair, or both? How much time/commitment can you invest?
- Consider Your Gender: Propecia is for men only. Rogaine and many alternatives are suitable for women.
- Assess Risk Tolerance: Are you comfortable with potential finasteride side effects? Do you prefer topical or oral treatments?
- Budget: Factor in costs (medications, devices, procedures, ongoing maintenance). Insurance rarely covers cosmetic hair loss treatments.
- Be Patient & Realistic: All treatments take time (6-12+ months) and consistency. Results vary. No treatment restores a full head of hair instantly or in advanced cases. Managing expectations is key.
The Bottom Line:
Propecia and Rogaine remain the cornerstones of evidence-based medical hair loss treatment, with the combination offering the best potential results for men. However, alternatives like LLLT, PRP, ketoconazole shampoo, and microneedling provide valuable adjunctive or alternative options, especially for those seeking non-pharmaceutical approaches or when medications aren’t suitable. Hair transplants offer a permanent surgical solution for advanced cases. The most effective strategy often involves a personalized plan developed with a dermatologist, combining medical treatments with supportive therapies and realistic expectations. Start early, be consistent, and don’t lose hope – effective management is possible